
When most people think of belly fat, they picture it as a stubborn layer that ruins their shape and makes it difficult to fit into their favorite clothes. While this is true, the issue of belly fat runs much deeper than just appearances. Many people don’t realize that belly fat isn’t just a passive storage of calories; it’s an active tissue that releases its own hormones and chemicals, affecting your overall health in ways you may not have considered.
Researchers now call belly fat a “hormone factory” that can either improve or harm your health, based on how much of it you have. Let’s explore the interesting and concerning truth about belly fat and why reducing it is more important than you think.
What Makes Belly Fat Different from Other Fat?
Not all fat in your body is the same. Fat that builds up around the arms, thighs, or hips is mostly subcutaneous fat, stored just under the skin. While it may influence your appearance, it’s not as damaging to your health.
Belly fat, however, includes a type called visceral fat. This fat is not only beneath your skin; it surrounds important organs like your liver, pancreas, and intestines. Due to its location, visceral fat has a significant impact on how your body functions.
Unlike regular fat, visceral belly fat acts almost like a separate organ, releasing a mix of hormones and chemicals into your bloodstream.
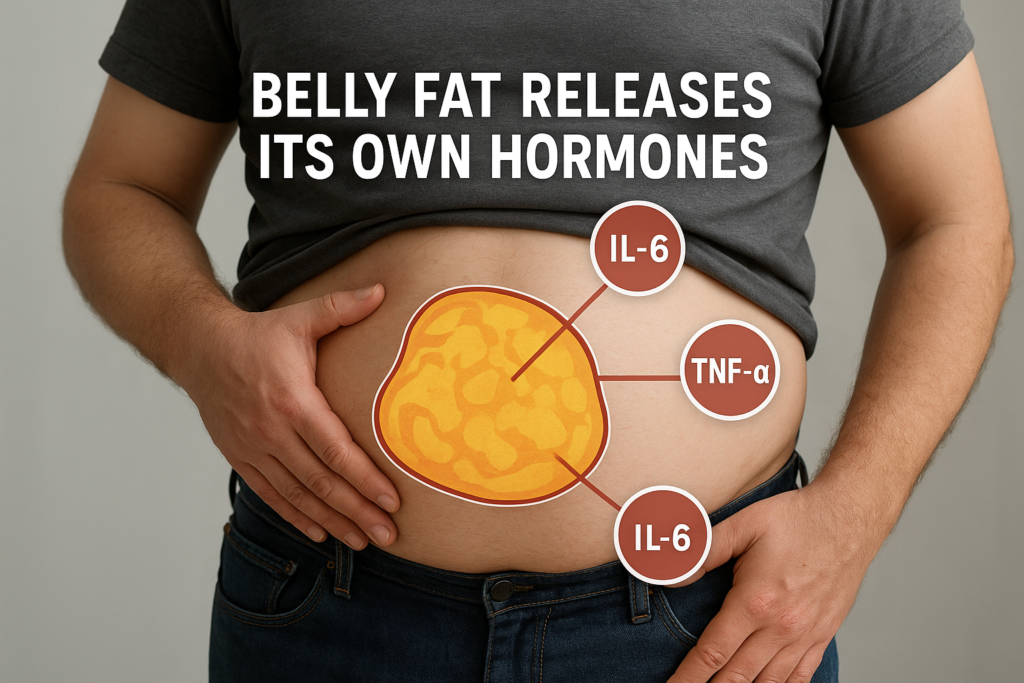
The Hormones Secreted by Belly Fat
Belly fat releases several adipokines, which are hormone-like substances and inflammatory chemicals that disrupt your body’s natural balance. Some of these include:
- Leptin: Normally, this hormone signals the brain when you are full. However, excess belly fat leads to leptin resistance, so your brain no longer receives the “I’m full” message. The result is constant hunger and overeating.
- Adiponectin: This hormone helps regulate blood sugar and fat metabolism. Ironically, the more belly fat you have, the less adiponectin your body produces, which makes weight gain and diabetes more likely.
- Cytokines: like TNF-alpha and IL-6. These are inflammatory chemicals that belly fat releases. They increase inflammation throughout the body, raising the risk of heart disease, arthritis, and even certain cancers.
- Resistin: This hormone is linked to insulin resistance, making it harder for your body to manage blood sugar effectively.
How These Hormones Affect Your Health?
The release of these hormones and chemicals from belly fat starts a chain reaction in your body. Some of the key health effects include:
- Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes: Excess belly fat makes your body less responsive to insulin, causing blood sugar levels to rise. Over time, this leads to type 2 diabetes.
- Chronic Inflammation: The inflammatory chemicals released by visceral fat keep your immune system on high alert. This constant, low-grade inflammation damages blood vessels, joints, and organs.
- Heart Disease and Stroke: Belly fat increases LDL, or bad cholesterol, while lowering HDL, or good cholesterol. Combined with inflammation, this speeds up plaque buildup in arteries, raising the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Since belly fat disrupts leptin and adiponectin, it creates a cycle of hunger, fat storage, and slow metabolism, making it harder to lose weight.
Why Belly Fat Is So Hard to Lose?
Many people find that belly fat is the most difficult to lose, even when they exercise and follow a diet. This occurs because visceral fat has more receptors for cortisol, the stress hormone, than other types of fat. High stress leads to increased cortisol, which pushes the body to store more fat around the belly. That’s why managing stress is just as important as diet and exercise for trimming your waistline.
How to Reduce Belly Fat and Regain Control?
The good news is that belly fat can be reduced with the right strategies. Here are some proven methods:
- Prioritize Sleep: Getting less than 6 hours of sleep a night raises cortisol and belly fat. Aim for 7 to 8 hours of quality rest.
- Manage Stress: Try meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to lower cortisol levels.
- Eat Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Focus on whole foods like fruits, vegetables, nuts, and fatty fish while cutting back on processed foods and sugar.
- Strength Training and Cardio: Combining weightlifting with high-intensity interval training (HIIT) is effective for burning visceral fat faster.
- Limit Alcohol: Drinking too much contributes directly to belly fat, often referred to as a “beer belly.”
- Regular use of Keyslim drops: In my personal opinion, this is a very good product to reduce belly fat naturally. At first, I was unsure about trying another supplement. However, KeySlim Drops really surprised me. Within a few weeks, I felt lighter and more energetic. I even noticed that my sleep improved. What impressed me the most was how easy it was. I could actually see and feel real changes in my body without going on strict diets or doing intense workouts. For me, KeySlim Drops have been more than just a weight loss aid. They have been the first step toward a healthier and happier lifestyle.
Click here to know more details about Keyslim drops
Final Thoughts
Belly fat is not just a cosmetic issue—it impacts your health. Belly fat releases its own hormones, making it one of the most dangerous types of fat in the body. If left unchecked, it can raise the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and other serious health problems.
The key takeaway? Don’t overlook your belly fat. Treat it like the active tissue it is, and make lifestyle changes to keep it under control. By reducing belly fat, you not only improve your appearance but also take an important step toward protecting your long-term health.